|

|
DACS: Main Application | 
|
|
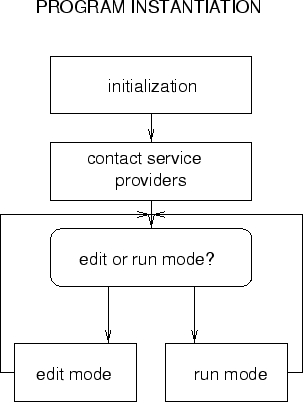
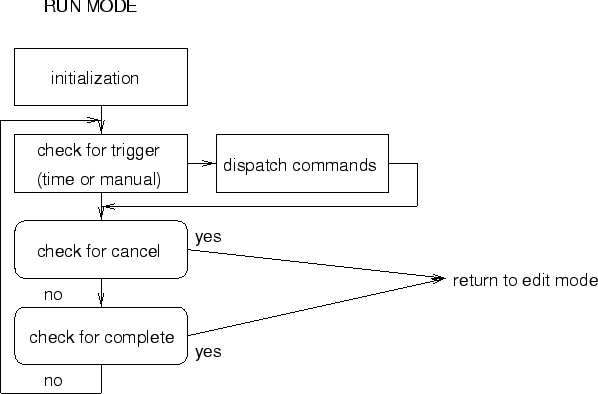
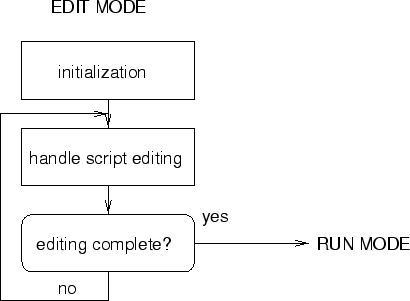
Next: Software Graphical User Interface Up: Functional Design Previous: Service Providers Contents Main ApplicationWhen the q2q program is started, it initializes, and then immediately attempts to contact all service providers. Upon completion of this, it enters one of two states, selected by the user. Edit mode allows interactive editing of audio scripts, and they are executed in run mode. Figure 109 shows this top level of program flow. In the run level, the program waits for cue triggers, be they manual or timed. These triggers come from DACS service providers, such as the control board service, the MIDI service (for SMPTE clock over MIDI), etc. If it finds that a trigger has occurred, the appropriate commands for that audio script are dispatched to service providers. This loop continues until the user chooses to cancel, or the script completes. Figure 110 shows this flow diagram. In the edit mode, the program allows the audio script to be edited. This editing can take place via the GUI or through the control board. The details of this editing are not covered in-depth here. A simple loop in which the editing takes place is run. This loop continues until the user enters the run mode. Figure 111 shows this flow diagram.Next: Software Graphical User Interface Up: Functional Design Previous: Service Providers Contents Steve Richardson 2000-07-06 |
Table of Contents
| |